tcache
tcache 是 glibc 2.26 (ubuntu 17.10) 之后引入的一种技术(see commit),目的是提升堆管理的性能。但提升性能的同时舍弃了很多安全检查,也因此有了很多新的利用方式。
主要参考了 glibc 源码,angelboy 的 slide 以及 tukan.farm,链接都放在最后了。
相关结构体
tcache 引入了两个新的结构体,tcache_entry 和 tcache_perthread_struct。
这其实和 fastbin 很像,但又不一样。
tcache_entry
/* We overlay this structure on the user-data portion of a chunk when
the chunk is stored in the per-thread cache. */
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;tcache_entry 用于链接空闲的 chunk 结构体,其中的 next 指针指向下一个大小相同的 chunk。
需要注意的是这里的 next 指向 chunk 的 user data,而 fastbin 的 fd 指向 chunk 开头的地址。
而且,tcache_entry 会复用空闲 chunk 的 user data 部分。
tcache_perthread_struct
每个 thread 都会维护一个 tcache_perthread_struct,它是整个 tcache 的管理结构,一共有 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 个计数器和 TCACHE_MAX_BINS项 tcache_entry,其中
tcache_entry用单向链表的方式链接了相同大小的处于空闲状态(free 后)的 chunk,这一点上和 fastbin 很像。counts记录了tcache_entry链上空闲 chunk 的数目,每条链上最多可以有 7 个 chunk。
用图表示大概是:
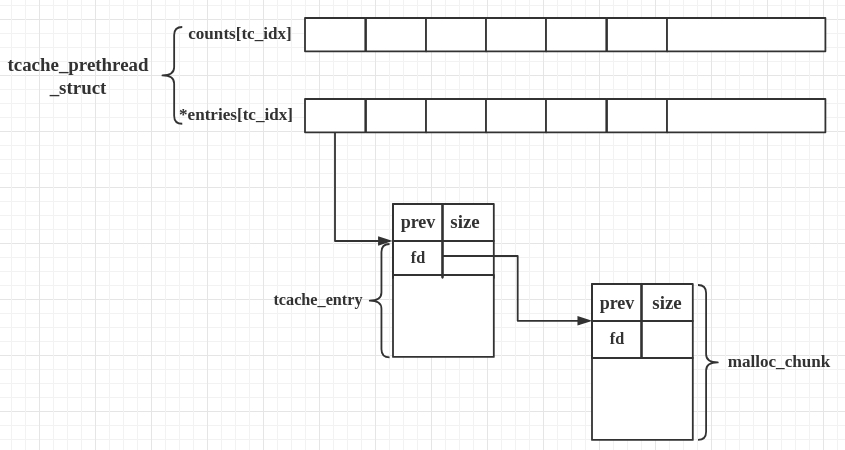
基本工作方式
第一次 malloc 时,会先 malloc 一块内存用来存放
tcache_perthread_struct。free 内存,且 size 小于 small bin size 时
tcache 之前会放到 fastbin 或者 unsorted bin 中
tcache 后:
先放到对应的 tcache 中,直到 tcache 被填满(默认是 7 个)
tcache 被填满之后,再次 free 的内存和之前一样被放到 fastbin 或者 unsorted bin 中
tcache 中的 chunk 不会合并(不取消 inuse bit)
malloc 内存,且 size 在 tcache 范围内
先从 tcache 取 chunk,直到 tcache 为空
tcache 为空后,从 bin 中找
tcache 为空时,如果
fastbin/smallbin/unsorted bin中有 size 符合的 chunk,会先把fastbin/smallbin/unsorted bin中的 chunk 放到 tcache 中,直到填满。之后再从 tcache 中取;因此 chunk 在 bin 中和 tcache 中的顺序会反过来
源码分析
接下来从源码的角度分析一下 tcache。
__libc_malloc
第一次 malloc 时,会进入到 MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE ()
__tcache_init()
其中 MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE () 在 tcache 为空(即第一次 malloc)时调用了 tcache_init(),直接查看 tcache_init()
tcache_init() 成功返回后,tcache_perthread_struct 就被成功建立了。
申请内存
接下来将进入申请内存的步骤
在 tcache->entries 不为空时,将进入 tcache_get() 的流程获取 chunk,否则与 tcache 机制前的流程类似,这里主要分析第一种 tcache_get()。这里也可以看出 tcache 的优先级很高,比 fastbin 还要高( fastbin 的申请在没进入 tcache 的流程中)。
tcache_get()
看一下 tcache_get()
tcache_get() 就是获得 chunk 的过程了。可以看出这个过程还是很简单的,从 tcache->entries[tc_idx] 中获得第一个 chunk,tcache->counts 减一,几乎没有任何保护。
__libc_free()
看完申请,再看看有 tcache 时的释放
__libc_free() 没有太多变化,MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE () 在 tcache 不为空失去了作用。
_int_free()
跟进 _int_free()
判断 tc_idx 合法,tcache->counts[tc_idx] 在 7 个以内时,就进入 tcache_put(),传递的两个参数是要释放的 chunk 和该 chunk 对应的 size 在 tcache 中的下标。
tcache_put()
tcache_puts() 完成了把释放的 chunk 插入到 tcache->entries[tc_idx] 链表头部的操作,也几乎没有任何保护。并且 没有把 p 位置零。
参考
http://tukan.farm/2017/07/08/tcache/
https://github.com/bash-c/slides/blob/master/pwn_heap/tcache_exploitation.pdf
https://www.secpulse.com/archives/71958.html
Last updated